How To Add Space In Domain_9 Profile
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to have advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Deploying Roaming User Profiles
Applies to: Windows Server 2022, Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008 R2
This topic describes how to employ Windows Server to deploy Roaming User Profiles to Windows customer computers. Roaming User Profiles redirects user profiles to a file share and then that users receive the same operating system and application settings on multiple computers.
For a listing of recent changes to this topic, see the Change history section of this topic.
Important
Due to the security changes made in MS16-072, we updated Step four: Optionally create a GPO for Roaming User Profiles in this topic so that Windows can properly use the Roaming User Profiles policy (and non revert to local policies on affected PCs).
Important
User customizations to Start is lost after an Os in-place upgrade in the following configuration:
- Users are configured for a roaming profile
- Users are immune to brand changes to Start
As a result, the Start carte du jour is reset to the default of the new OS version later the OS in-identify upgrade. For workarounds, see Appendix C: Working around reset Get-go menu layouts later upgrades.
Prerequisites
Hardware requirements
Roaming User Profiles requires an x64-based or x86-based computer; it isn't supported by Windows RT.
Software requirements
Roaming User Profiles has the following software requirements:
-
If you lot are deploying Roaming User Profiles with Folder Redirection in an environment with existing local user profiles, deploy Folder Redirection before Roaming User Profiles to minimize the size of roaming profiles. Afterward the existing user folders have been successfully redirected, y'all tin can deploy Roaming User Profiles.
-
To administrate Roaming User Profiles, you must be signed in as a member of the Domain Administrators security group, the Enterprise Administrators security grouping, or the Group Policy Creator Owners security grouping.
-
Customer computers must run Windows 10, Windows viii.i, Windows 8, Windows vii, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008 R2, or Windows Server 2008.
-
Client computers must exist joined to the Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) that you lot are managing.
-
A calculator must be bachelor with Group Policy Management and Agile Directory Administration Center installed.
-
A file server must be bachelor to host roaming user profiles.
- If the file share uses DFS Namespaces, the DFS folders (links) must have a single target to forbid users from making conflicting edits on different servers.
- If the file share uses DFS Replication to replicate the contents with another server, users must be able to access only the source server to prevent users from making alien edits on different servers.
- If the file share is clustered, disable continuous availability on the file share to avoid performance issues.
-
To use principal computer back up in Roaming User Profiles, there are additional client computer and Active Directory schema requirements. For more data, see Deploy Primary Computers for Folder Redirection and Roaming User Profiles.
-
The layout of a user's Get-go menu won't roam on Windows 10, Windows Server 2019, or Windows Server 2016 if they're using more than one PC, Remote Desktop Session Host, or Virtualized Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) server. Every bit a workaround, you can specify a Beginning layout as described in this topic. Or you can make apply of user profile disks, which properly roam First bill of fare settings when used with Remote Desktop Session Host servers or VDI servers. For more info, see Easier User Data Management with User Profile Disks in Windows Server 2012.
Considerations when using Roaming User Profiles on multiple versions of Windows
If you make up one's mind to use Roaming User Profiles across multiple versions of Windows, nosotros recommend taking the following actions:
- Configure Windows to maintain separate profile versions for each operating system version. This helps prevent undesirable and unpredictable issues such as profile corruption.
- Use Binder Redirection to shop user files such as documents and pictures outside of user profiles. This enables the same files to exist available to users across operating system versions. It too keeps profiles small and sign-ins quick.
- Classify sufficient storage for Roaming User Profiles. If you support two operating system versions, profiles will double in number (and thus full space consumed) because a separate profile is maintained for each operating organization version.
- Don't utilize Roaming User Profiles across computers running Windows Vista/Windows Server 2008 and Windows 7/Windows Server 2008 R2. Roaming between these operating organisation versions isn't supported due to incompatibilities in their profile versions.
- Inform your users that changes made on one operating organization version won't roam to another operating system version.
- When moving your environment to a version of Windows that uses a different profile version (such as from Windows ten to Windows x, version 1607—see Appendix B: Profile version reference information for a list), users receive a new, empty roaming user profile. You can minimize the touch of getting a new contour past using Folder Redirection to redirect common folders. There isn't a supported method of migrating roaming user profiles from one profile version to another.
Stride 1: Enable the use of separate profile versions
If y'all are deploying Roaming User Profiles on computers running Windows eight.1, Windows eight, Windows Server 2012 R2, or Windows Server 2012, we recommend making a couple of changes to your Windows surround prior to deploying. These changes help ensure that time to come operating organization upgrades go smoothly, and facilitate the power to simultaneously run multiple versions of Windows with Roaming User Profiles.
To make these changes, apply the following procedure.
-
Download and install the advisable software update on all computers on which you're going to use roaming, mandatory, super-mandatory, or domain default profiles:
- Windows eight.1, or Windows Server 2012 R2: install the software update described in article 2887595 in the Microsoft Knowledge Base (when released).
- Windows 8 or Windows Server 2012: install the software update described in article 2887239 in the Microsoft Knowledge Base.
-
On all computers running Windows eight.1, Windows 8, Windows Server 2012 R2, or Windows Server 2012 on which you will use Roaming User Profiles, use Registry Editor or Group Policy to create the post-obit registry key DWORD Value and set it to
1. For information well-nigh creating registry keys past using Grouping Policy, see Configure a Registry Item.HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Organization\CurrentControlSet\Services\ProfSvc\Parameters\UseProfilePathExtensionVersionWarning
Incorrectly editing the registry may severely damage your organization. Before making changes to the registry, you should support any valued data on the computer.
-
Restart the computers.
Step 2: Create a Roaming User Profiles security group
If your environs is non already fix with Roaming User Profiles, the beginning step is to create a security grouping that contains all users and/or computers to which you desire to utilize Roaming User Profiles policy settings.
- Administrators of general-purpose roaming user profiles deployments typically create a security grouping for users.
- Administrators of Remote Desktop Services or virtualized desktop deployments typically use a security grouping for users and the shared computers.
Hither's how to create a security group for Roaming User Profiles:
-
Open Server Manager on a computer with Active Directory Administration Eye installed.
-
On the Tools menu, select Active Directory Administration Heart. Active Directory Administration Center appears.
-
Right-click the appropriate domain or OU, select New, and and so select Group.
-
In the Create Grouping window, in the Group section, specify the following settings:
- In Group name, type the name of the security grouping, for instance: Roaming User Profiles Users and Computers.
- In Grouping scope, select Security, and and then select Global.
-
In the Members section, select Add. The Select Users, Contacts, Computers, Service Accounts or Groups dialog box appears.
-
If yous desire to include figurer accounts in the security group, select Object Types, select the Computers cheque box then select OK.
-
Type the names of the users, groups, and/or computers to which you want to deploy Roaming User Profiles, select OK, and then select OK again.
If you lot do not already have a divide file share for roaming user profiles (contained from any shares for redirected folders to prevent inadvertent caching of the roaming profile binder), use the following process to create a file share on a server running Windows Server.
Note
Some functionality might differ or exist unavailable depending on the version of Windows Server you're using.
Hither's how to create a file share on Windows Server:
-
In the Server Director navigation pane, select File and Storage Services, and then select Shares to display the Shares folio.
-
In the Shares tile, select Tasks, and then select New Share. The New Share Wizard appears.
-
On the Select Profile folio, select SMB Share – Quick. If yous have File Server Resource Manager installed and are using folder management properties, instead select SMB Share - Advanced.
-
On the Share Location page, select the server and volume on which you desire to create the share.
-
On the Share Name page, type a name for the share (for example, User Profiles$) in the Share name box.
Tip
When creating the share, hibernate the share by putting a
$afterwards the share name. This hides the share from casual browsers. -
On the Other Settings page, clear the Enable continuous availability checkbox, if present, and optionally select the Enable admission-based enumeration and Encrypt information access checkboxes.
-
On the Permissions page, select Customize permissions…. The Advanced Security Settings dialog box appears.
-
Select Disable inheritance, so select Convert inherited permissions into explicit permission on this object.
-
Set up the permissions as described in Required permissions for the file share hosting roaming user profiles and shown in the following screen shot, removing permissions for unlisted groups and accounts, and adding special permissions to the Roaming User Profiles Users and Computers grouping that you created in Step 1.
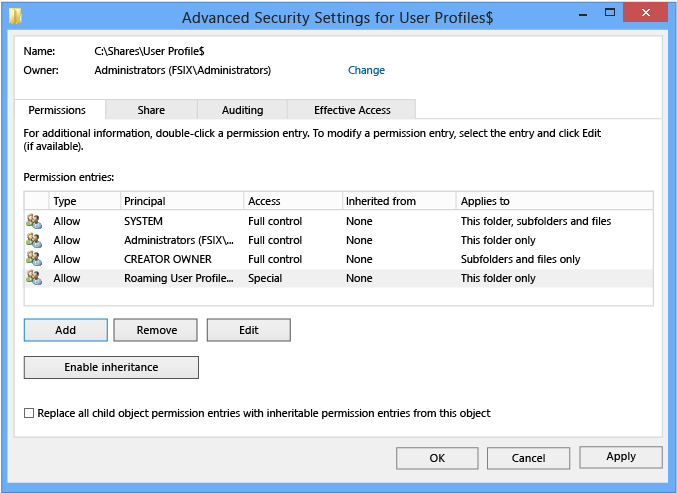
Figure 1 Setting the permissions for the roaming user profiles share
-
If you chose the SMB Share - Advanced profile, on the Management Properties page, select the User Files Binder Usage value.
-
If you chose the SMB Share - Advanced profile, on the Quota folio, optionally select a quota to utilise to users of the share.
-
On the Confirmation page, select Create.
| User Account | Access | Applies to |
|---|---|---|
| System | Full control | This folder, subfolders and files |
| Administrators | Total Control | This folder only |
| Creator/Owner | Full Control | Subfolders and files only |
| Security group of users needing to put data on share (Roaming User Profiles Users and Computers) | List folder / read data (Advanced permissions) Create folders / append data (Advanced permissions) | This folder only |
| Other groups and accounts | None (remove) |
Step 4: Optionally create a GPO for Roaming User Profiles
If you practice not already take a GPO created for Roaming User Profiles settings, use the post-obit procedure to create an empty GPO for utilise with Roaming User Profiles. This GPO allows you to configure Roaming User Profiles settings (such as primary computer back up, which is discussed separately), and can also be used to enable Roaming User Profiles on computers, as is typically done when deploying in virtualized desktop environments or with Remote Desktop Services.
Here's how to create a GPO for Roaming User Profiles:
-
Open Server Manager on a computer with Grouping Policy Management installed.
-
From the Tools card select Group Policy Direction. Group Policy Management appears.
-
Right-click the domain or OU in which yous desire to setup Roaming User Profiles, then select Create a GPO in this domain, and Link information technology here.
-
In the New GPO dialog box, type a name for the GPO (for example, Roaming User Profile Settings), and and so select OK.
-
Right-click the newly created GPO and then articulate the Link Enabled checkbox. This prevents the GPO from being applied until y'all cease configuring information technology.
-
Select the GPO. In the Security Filtering department of the Telescopic tab, select Authenticated Users, and so select Remove to forestall the GPO from being practical to everyone.
-
In the Security Filtering section, select Add.
-
In the Select User, Computer, or Group dialog box, type the name of the security group yous created in Step 1 (for instance, Roaming User Profiles Users and Computers), and so select OK.
-
Select the Delegation tab, select Add, blazon Authenticated Users, select OK, so select OK again to accept the default Read permissions.
This pace is necessary due to security changes fabricated in MS16-072.
Important
Due to the security changes made in MS16-072A, y'all now must give the Authenticated Users group delegated Read permissions to the GPO - otherwise the GPO won't go applied to users, or if information technology's already applied, the GPO is removed, redirecting user profiles back to the local PC. For more info, see Deploying Group Policy Security Update MS16-072.
Step v: Optionally fix Roaming User Profiles on user accounts
If you are deploying Roaming User Profiles to user accounts, employ the following procedure to specify roaming user profiles for user accounts in Active Directory Domain Services. If you are deploying Roaming User Profiles to computers, as is typically washed for Remote Desktop Services or virtualized desktop deployments, instead use the process documented in Stride six: Optionally prepare up Roaming User Profiles on computers.
Note
If you set Roaming User Profiles on user accounts by using Agile Directory and on computers past using Group Policy, the computer-based policy setting takes precedence.
Here's how to set up Roaming User Profiles on user accounts:
-
In Active Directory Administration Center, navigate to the Users container (or OU) in the advisable domain.
-
Select all users to which you desire to assign a roaming user profile, correct-click the users and and so select Backdrop.
-
In the Profile department, select the Profile path: checkbox and then enter the path to the file share where you want to store the user's roaming user profile, followed by
%username%(which is automatically replaced with the user name the start fourth dimension the user signs in). For example:\\fs1.corp.contoso.com\User Profiles$\%username%To specify a mandatory roaming user profile, specify the path to the NTuser.man file that yous created previously, for example,
fs1.corp.contoso.comUser Profiles$default. For more than information, run into Create mandatory user profiles. -
Select OK.
Annotation
To remove restrictions on app deployment for special profiles, enable the Permit deployment operations in special profiles policy setting (located in Calculator Configuration\Policies\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\App Package Deployment). Still, deployed apps in this scenario will leave some information stored on the computer, which could accumulate, for example, if there are hundreds of users of a unmarried computer. To make clean up apps, locate or develop a tool that uses the CleanupPackageForUserAsync API to clean upwardly app packages for users who no longer have a profile on the computer.
For additional background information about Windows Store apps, see Manage Client Admission to the Windows Shop.
Step 6: Optionally set up Roaming User Profiles on computers
If you are deploying Roaming User Profiles to computers, as is typically washed for Remote Desktop Services or virtualized desktop deployments, use the post-obit procedure. If you are deploying Roaming User Profiles to user accounts, instead utilise the process described in Step v: Optionally set up Roaming User Profiles on user accounts.
You tin can apply Group Policy to utilize Roaming User Profiles to computers running Windows 8.1, Windows viii, Windows 7, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008 R2, or Windows Server 2008.
Note
If you lot gear up Roaming User Profiles on computers by using Group Policy and on user accounts by using Active Directory, the computer-based policy setting takes precedence.
Here's how to set up Roaming User Profiles on computers:
-
Open Server Managing director on a computer with Grouping Policy Management installed.
-
From the Tools menu, select Grouping Policy Direction. Group Policy Management volition appear.
-
In Group Policy Management, right-click the GPO you lot created in Pace 3 (for example, Roaming User Profiles Settings), and then select Edit.
-
In the Group Policy Direction Editor window, navigate to Computer Configuration, then Policies, then Administrative Templates, then Organisation, and and then User Profiles.
-
Right-click Set roaming contour path for all users logging onto this computer and then select Edit.
Tip
A user's habitation binder, if configured, is the default binder used by some programs such as Windows PowerShell. You can configure an alternative local or network location on a per-user footing by using the Home folder section of the user business relationship properties in AD DS. To configure the abode folder location for all users of a calculator running Windows 8.i, Windows 8, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, or Windows Server 2012 in a virtual desktop environment, enable the Set user dwelling house binder policy setting, and then specify the file share and drive letter of the alphabet to map (or specify a local binder). Do non use environment variables or ellipses. The user'due south allonym is appended to the end of the path specified during user sign on.
-
In the Backdrop dialog box, select Enabled
-
In the Users logging onto this computer should use this roaming profile path box, enter the path to the file share where yous want to store the user's roaming user contour, followed by
%username%(which is automatically replaced with the user proper noun the first time the user signs in). For instance:\\fs1.corp.contoso.com\User Profiles$\%username%To specify a mandatory roaming user profile, which is a preconfigured profile to which users cannot make permanent changes (changes are reset when the user signs out), specify the path to the NTuser.man file that you created previously, for case,
\\fs1.corp.contoso.com\User Profiles$\default. For more information, run into Creating a Mandatory User Profile. -
Select OK.
Step 7: Optionally specify a Start layout for Windows 10 PCs
Y'all tin employ Group Policy to apply a specific Start bill of fare layout so that users see the same Start layout on all PCs. If users sign in to more than than one PC and you want them to have a consistent Offset layout across PCs, make certain that the GPO applies to all of their PCs.
To specify a Offset layout, practice the following:
- Update your Windows x PCs to Windows ten version 1607 (also known every bit the Anniversary Update) or newer, and install the March 14th, 2017 cumulative update (KB4013429) or newer.
- Create a full or partial Start menu layout XML file. To do so, run across Customize and export Start layout.
- If you specify a total Start layout, a user tin can't customize any part of the Start carte du jour. If you specify a partial Start layout, users can customize everything simply the locked groups of tiles you specify. However, with a partial Showtime layout, user customizations to the First carte du jour won't roam to other PCs.
- Apply Group Policy to apply the customized Get-go layout to the GPO you created for Roaming User Profiles. To do so, run across Utilise Group Policy to apply a customized Showtime layout in a domain.
- Use Group Policy to set the post-obit registry value on your Windows 10 PCs. To do so, run into Configure a Registry Particular.
| Activeness | Update |
|---|---|
| Hive | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE |
| Key path | Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer |
| Value proper name | SpecialRoamingOverrideAllowed |
| Value blazon | REG_DWORD |
| Value data | 1 (or 0 to disable) |
| Base | Decimal |
- (Optional) Enable first-fourth dimension logon optimizations to make signing in faster for users. To do then, see Employ policies to better sign-in time.
- (Optional) Farther subtract sign-in times by removing unnecessary apps from the Windows x base of operations image you lot use to deploy client PCs. Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server 2016 don't take any pre-provisioned apps, and so you can skip this step on server images.
-
To remove apps, employ the Remove-AppxProvisionedPackage cmdlet in Windows PowerShell to uninstall the following applications. If your PCs are already deployed you tin script the removal of these apps using the Remove-AppxPackage.
- Microsoft.windowscommunicationsapps_8wekyb3d8bbwe
- Microsoft.BingWeather_8wekyb3d8bbwe
- Microsoft.DesktopAppInstaller_8wekyb3d8bbwe
- Microsoft.Getstarted_8wekyb3d8bbwe
- Microsoft.Windows.Photos_8wekyb3d8bbwe
- Microsoft.WindowsCamera_8wekyb3d8bbwe
- Microsoft.WindowsFeedbackHub_8wekyb3d8bbwe
- Microsoft.WindowsStore_8wekyb3d8bbwe
- Microsoft.XboxApp_8wekyb3d8bbwe
- Microsoft.XboxIdentityProvider_8wekyb3d8bbwe
- Microsoft.ZuneMusic_8wekyb3d8bbwe
-
Note
Uninstalling these apps decreases sign-in times, simply you tin can go out them installed if your deployment needs whatsoever of them.
Step 8: Enable the Roaming User Profiles GPO
If you prepare up Roaming User Profiles on computers by using Group Policy, or if you lot customized other Roaming User Profiles settings by using Group Policy, the next stride is to enable the GPO, permitting it to be applied to affected users.
Here's how to enable the Roaming User Profile GPO:
- Open Group Policy Management.
- Right-click the GPO that you created and then select Link Enabled. A checkbox appears adjacent to the card item.
Stride ix: Test Roaming User Profiles
To test Roaming User Profiles, sign in to a computer with a user account configured for Roaming User Profiles, or sign in to a computer configured for Roaming User Profiles. Then confirm that the profile is redirected.
Here's how to test Roaming User Profiles:
-
Sign in to a principal estimator (if you enabled chief computer support) with a user business relationship for which you have enabled Roaming User Profiles enabled. If yous enabled Roaming User Profiles on specific computers, sign in to ane of these computers.
-
If the user has previously signed in to the computer, open an elevated command prompt, so type the following command to ensure that the latest Group Policy settings are applied to the client computer:
GpUpdate /Forcefulness -
To confirm that the user profile is roaming, open Control Panel, select Organization and Security, select System, select Advanced Arrangement Settings, select Settings in the User Profiles section and so look for Roaming in the Blazon cavalcade.
Appendix A: Checklist for deploying Roaming User Profiles
| Condition | Activity |
|---|---|
| ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ | 1. Prepare domain - Join computers to domain - Enable the apply of separate contour versions - Create user accounts - (Optional) Deploy Binder Redirection |
| ☐ | 2. Create security group for Roaming User Profiles - Group proper name: - Members: |
| ☐ | three. Create a file share for Roaming User Profiles - File share name: |
| ☐ | 4. Create a GPO for Roaming User Profiles - GPO name: |
| ☐ | 5. Configure Roaming User Profiles policy settings |
| ☐ ☐ ☐ | six. Enable Roaming User Profiles - Enabled in AD DS on user accounts? - Enabled in Group Policy on calculator accounts? |
| ☐ | 7. (Optional) Specify a mandatory Get-go layout for Windows x PCs |
| ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ | viii. (Optional) Enable primary computer back up - Designate principal computers for users - Location of user and primary figurer mappings: - (Optional) Enable primary computer support for Folder Redirection - Estimator-based or User-based? - (Optional) Enable primary reckoner back up for Roaming User Profiles |
| ☐ | 9. Enable the Roaming User Profiles GPO |
| ☐ | 10. Exam Roaming User Profiles |
Appendix B: Contour version reference information
Each profile has a contour version that corresponds roughly to the version of Windows on which the profile is used. For example, Windows 10, version 1703 and version 1607 both employ the .V6 contour version. Microsoft creates a new profile version only when necessary to maintain compatibility, which is why not every version of Windows includes a new contour version.
The post-obit table lists the location of Roaming User Profiles on various versions of Windows.
| Operating organization version | Roaming User Profile location |
|---|---|
| Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 | \\<servername>\<fileshare>\<username> |
| Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 | \\<servername>\<fileshare>\<username>.V2 |
| Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 | \\<servername>\<fileshare>\<username>.V2 |
| Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 | \\<servername>\<fileshare>\<username>.V3 (later the software update and registry key are applied)\\<servername>\<fileshare>\<username>.V2 (before the software update and registry key are applied) |
| Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 | \\<servername>\<fileshare>\<username>.V4 (after the software update and registry key are practical)\\<servername>\<fileshare>\<username>.V2 (before the software update and registry fundamental are applied) |
| Windows ten | \\<servername>\<fileshare>\<username>.V5 |
| Windows 10, version 1703 and version 1607 | \\<servername>\<fileshare>\<username>.V6 |
Appendix C: Working around reset Showtime menu layouts after upgrades
Here are some means to work around Kickoff menu layouts getting reset later an in-place upgrade:
-
If merely one user ever uses the device and the Information technology Admin uses a managed OS deployment strategy such as Configuration Manager they tin do the following:
-
Export the Beginning carte layout with Export-Startlayout earlier the upgrade
-
Import the First card layout with Import-StartLayout after OOBE merely earlier the user signs in
Note
Importing a StartLayout modifies the Default User profile. All user profiles created afterwards the import has occurred will get the imported Start-Layout.
-
-
It Admins can opt to manage Start'due south Layout with Group Policy. Using Group Policy provides a centralized management solution to utilize a standardized Start Layout to users. In that location are 2 modes to modes to using Group Policy for Showtime management. Full Lockdown and Partial Lockdown. The full lockdown scenario prevents the user from making any changes to Start's layout. The partial lockdown scenario allows user to brand changes to a specific area of Commencement. For more info, run into Customize and export Start layout.
Note
User made changes in the fractional lockdown scenario will still be lost during upgrade.
-
Let the Start layout reset occur and allow end users to reconfigure Starting time. A notification email or other notification can be sent to end users to await their Showtime layouts to exist reset after the OS upgrade to minimized impact.
Modify history
The following table summarizes some of the most important changes to this topic.
| Date | Description | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| May 1st, 2019 | Added updates for Windows Server 2019 | |
| Apr 10th, 2018 | Added discussion of when user customizations to Offset are lost afterwards an OS in-place upgrade | Callout known issue. |
| March 13th, 2018 | Updated for Windows Server 2016 | Moved out of Previous Versions library and updated for electric current version of Windows Server. |
| April 13th, 2017 | Added contour data for Windows ten, version 1703, and clarified how roaming profile versions piece of work when upgrading operating systems—meet Considerations when using Roaming User Profiles on multiple versions of Windows. | Client feedback. |
| March 14th, 2017 | Added optional step for specifying a mandatory Start layout for Windows 10 PCs in Appendix A: Checklist for deploying Roaming User Profiles. | Feature changes in latest Windows update. |
| January 23rd, 2017 | Added a pace to Pace four: Optionally create a GPO for Roaming User Profiles to consul Read permissions to Authenticated Users, which is now required because of a Grouping Policy security update. | Security changes to Group Policy processing. |
| Dec 29th, 2016 | Added a link in Step 8: Enable the Roaming User Profiles GPO to make it easier to get info on how to set up Group Policy for chief computers. Also stock-still a couple references to steps 5 and 6 that had the numbers incorrect. | Client feedback. |
| December fifth, 2016 | Added info explaining a Start bill of fare settings roaming consequence. | Customer feedback. |
| July 6th, 2016 | Added Windows 10 profile version suffixes in Appendix B: Profile version reference information. As well removed Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 from the list of supported operating systems. | Updates for the new versions of Windows, and removed info about versions of Windows that are no longer supported. |
| July 7th, 2015 | Added requirement and step to disable continuous availability when using a clustered file server. | Amassed file shares have better functioning for modest writes (which are typical with roaming user profiles) when continuous availability is disabled. |
| March 19th, 2014 | Capitalized contour version suffixes (.V2, .V3, .V4) in Appendix B: Contour version reference information. | Although Windows is case insensitive, if you lot utilize NFS with the file share, it'south of import to have the correct (uppercase) capitalization for the profile suffix. |
| October ninth, 2013 | Revised for Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1, clarified a few things, and added the Considerations when using Roaming User Profiles on multiple versions of Windows and Appendix B: Profile version reference information sections. | Updates for new version; customer feedback. |
More information
- Deploy Binder Redirection, Offline Files, and Roaming User Profiles
- Deploy Chief Computers for Binder Redirection and Roaming User Profiles
- Implementing User Land Direction
- Microsoft'south Support Statement Effectually Replicated User Profile Data
- Sideload Apps with DISM
- Troubleshooting packaging, deployment, and query of Windows Runtime-based apps
Feedback
Submit and view feedback for
How To Add Space In Domain_9 Profile,
Source: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/storage/folder-redirection/deploy-roaming-user-profiles
Posted by: puckettsectirepas.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Add Space In Domain_9 Profile"
Post a Comment